Impact sound and airborne sound
What is impact sound and airborne sound and how does it affect your indoor environment?
Impact sound
Impact sound is one of the most disturbing sounds that can occur in buildings. Studies show that impact sound is one of the most common complaints in homes and affects the comfort and well-being of many people. When someone walks on the floor of the apartment or room above, the sound can travel through the building’s structure and become very disturbing for people on the floor below.
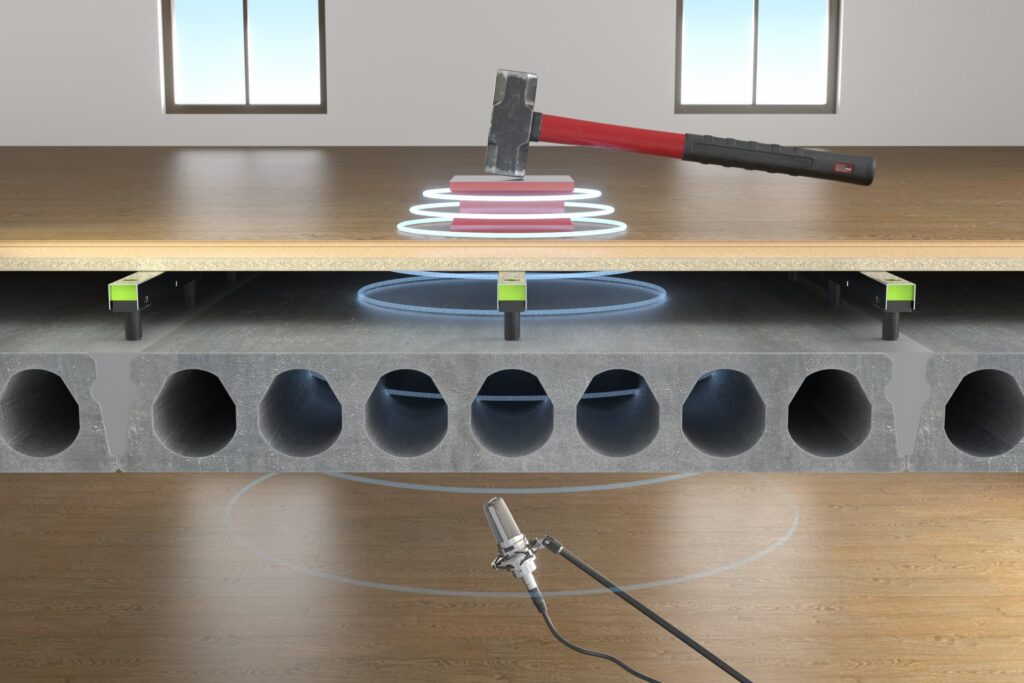

Why does impact sound occur in buildings?
Impact sound occurs when people move on floors and the sound is transmitted through the building structure. In older buildings, the problem is often more pronounced because impact sound insulation was not prioritised as it is today. Measurement of impact sound levels shows that the difference between different constructions can be significant. Standardised measurement provides values that help us understand how effective impact sound insulation is.
How is impact sound level measured in homes?
Impact sound level is measured according to standardised methods using a special hammer to create sound which is then measured in the room below. The lower the impact sound level, the better the sound insulation of the structure. The difference in impact sound level between different floors can determine the sound level in your home. Requirements for impact sound levels are also specified in the Swedish National Board of Housing, Building and Planning’s building regulations and apply to all new buildings.
Solutions to reduce annoying impact noise
If you want to reduce the risk of impact noise in your housing project, there are different solutions. The Granab system provides significantly improved sound insulation compared to other solutions and helps you create a quieter environment. By installing our sound-insulating subfloors, you can achieve impact sound insulation that makes the difference between a disturbing and a comfortable indoor environment.
The effect of the Granab Subfloor System on impact sound
The Granab system has been developed in close co-operation with acousticians and sound consultants to meet strikt requirements for impact and airborne sound insulation. The system acts as a sound-reducing complement to an otherwise lightweight building structure and shows very good results when measured. You get a comfortable floor that also reduces the level of impact sound and other disturbing noises between different rooms and floors.
What do the regulations say about impact sound?
According to the Swedish National Board of Housing, Building and Planning’s building regulations, buildings must be designed so that residents are protected from disturbing noise. Different types of premises are categorised into classes with different sound requirements depending on the type of activity that is relevant to the premises. Table 7:21a shows specific requirements for impact sound levels for dwellings. Standardised measurement according to SS 25267 helps you to verify that your project meets the requirements.
Sound classification description in living areas according to SS 25267
Sound class A: The sound class corresponds to very good acoustic conditions.
Sound class B: The sound class corresponds to significantly better acoustic conditions than sound class C. This sound class should be applied when a good living environment is requested and is the most common class.
Sound class C: The sound class provides satisfactory acoustic conditions for a majority of residents and can be applied as a minimum requirement according to the Swedish Board of Building, Planning and Housing’s directives.
Remarks: The functional requirements in this standard are adapted to the respective sound classes on the basis of extensive practical experience of subjectively perceived acoustic environments in dwellings. It should be noted, however, that building constructions – for both practical and financial reasons – cannot be designed to entirely avoid audible sound from adjoining spaces from all types of activities. Audible sound can occur, for example, from jumping or substantial impact on a floor. This may even occur in buildings that fulfil the higher sound classes.
Walking noise: Walking noise is addressed in SS 25268 (version 2 2007) and referred to there as ”impact sound in same room”.
The requirement stipulates that walking noise shall be limited in spaces in which several persons are present more than
temporarily, such as in large office spaces, nursery schools, etc. Guidelines for measurement and assessment of percussive
sound are included in the SIS technical report 2007:15 (www.sis.se). The degree of walking noise is dependent on the floor
covering used. Contact Granab for more information prior to planning.

Comfort and well-being through the right flooring choice
Do you want to know more about how you can improve impact sound insulation in your building project? With our expertise and help, you will have access to a wide range of solutions that will make the difference in sound levels between different rooms and floors.
What is airborne sound and how does it differ from impact sound?
Airborne sound is sound that travels through the air and is transmitted between rooms and floors through walls, ceilings and floors. Unlike impact sound, which is created by direct contact with floors, airborne sound is created by, for example, loud music, voices, TV sound or other sound sources travelling through the air. Both types of noise can have a negative impact on the sound environment.
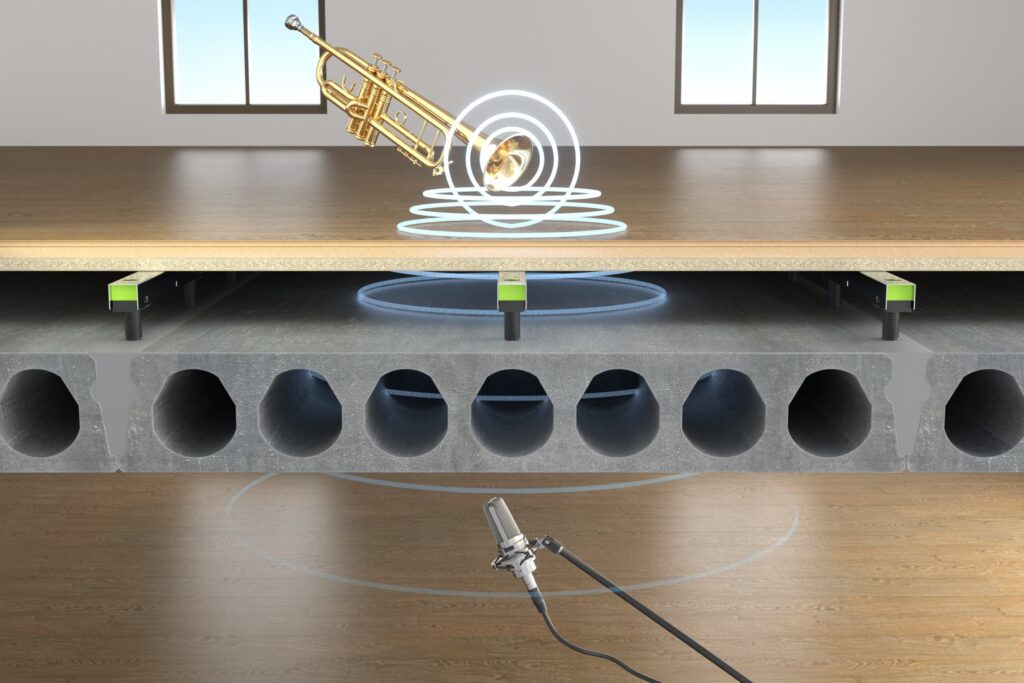

Measuring airborne sound insulation
Unlike the measurement of impact sound, where the aim is to achieve the lowest possible result, the measurement of airborne sound is carried out by measuring the difference in sound level between the transmitting and receiving rooms. The greater the difference and therefore the higher the result, the better the airborne sound insulation of the structure. To get an accurate measurement, the reverberation time in the receiving room and the background noise level are also taken into account.
This standardised measurement shows how effective the sound insulation is against different types of disturbing noise.
The Granab system has shown through extensive measurement that it provides improved airborne sound insulation according to the requirements of Swedish standards.
How are airborne and impact sounds related?
Impact sounds can also create airborne sound when people walk on the floor and is a type of structure-borne noise that propagates through the building. Footsteps cause vibrations that are transmitted through the building structure, such as floors and other structural elements, to neighbouring spaces. When these vibrations reach surfaces in the room below, such as ceilings and walls, these surfaces start to vibrate and act as sound sources, emitting airborne sound into the room.
This makes the problem twofold – you get both the direct impact sound through the joists and the airborne sound that propagates in the room.
Conditions
Granab subfloor systems, including floor coverings, can be configured for various sound requirements.
In order to fulfill the intended sound class between rooms in buildings with Granab subfloor systems in both vertical and horizontal directions,
it is important:
- That the slabs and walls provide suitable conditions, which can be verified by calculating the sound insulation of unfinished floors and walls according to EN 12354 or by measuring the sound insulation during the production phase according to the standard methods. Measurements are made before the underfloor system is installed with temporary actions taken during measurement to prevent airborne sound leakage between measurement spaces.
- That Granab subfloor systems are installed by trained installers and and in accordance with Granab’s installation instructions and checklists.
- That Granab systems and the floor coverings are floating and do not have rigid contact points against the building framework.
- That sound leakage through joints and installations in floors and walls is prevented.
- That flank transmission via attached constructions – exterior walls, subceilings, etc. – is prevented.
- That sound transmission via ventilation ducts between flats does not occur.
- For more information, see Granab’s general delivery and sales terms.


Impact and airborne sound reduction 3000N
Sound insulation measurements Granab subfloor system installed on HD/F 200 mm.
Accredited sound insulation measurements according to SS-EN ISO 140-4-7 performed by KM Akustikbyrån.
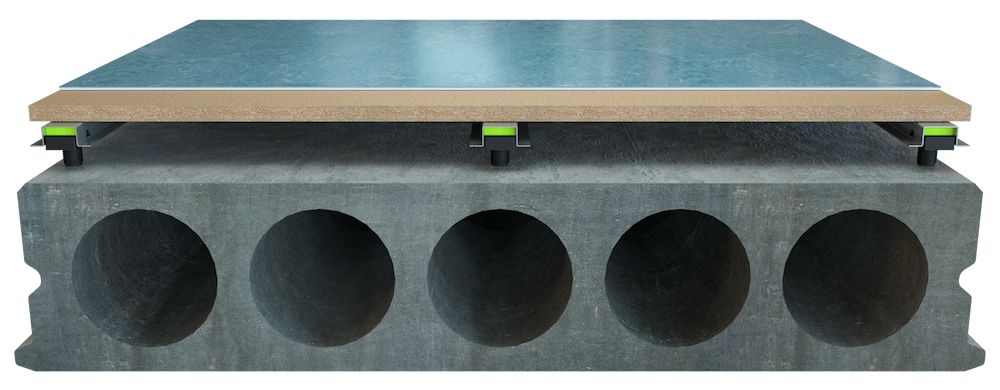
Design:
Granab subfloor system installed on HD/f 200mm and 22mm chipboard + carpet.
Result:
Impact sound: Lnw+c 43 dB, Airborne sound: Rw+c 65 dB.

Design:
Granab subfloor system installed on HD/f 200mm and 22mm chipboard + 15mm parquet.
Result:
Impact sound: Lnw+c 43 dB, Airborne sound: Rw+c 65 dB.
Impact and airborne sound reduction 7000N
Sound insulation measurements Granab subfloor system installed on HD/F 200 mm.
Accredited sound insulation measurements according to SS-EN ISO 140-4-7 performed by KM Akustikbyrån.
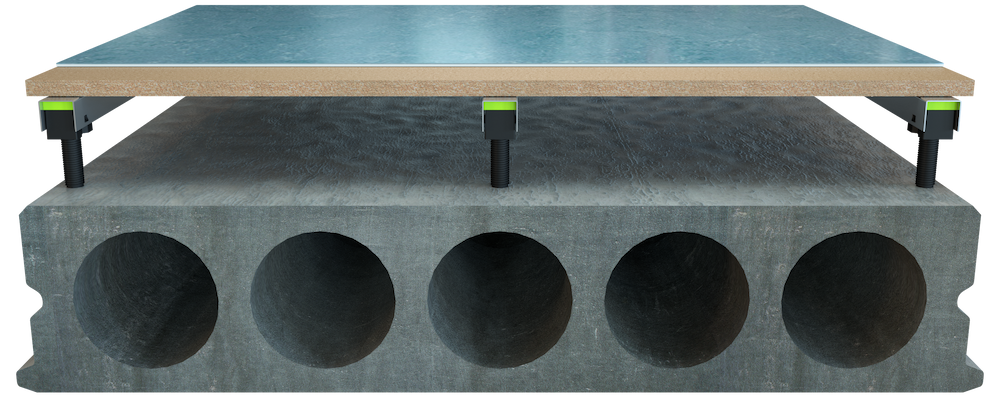
Design:
Granab subfloor system installed on HD/f 200mm and 22mm chipboard + carpet.
Result:
Impact sound: Lnw+c 50 dB, Airborne sound: Rw+c 59 dB.
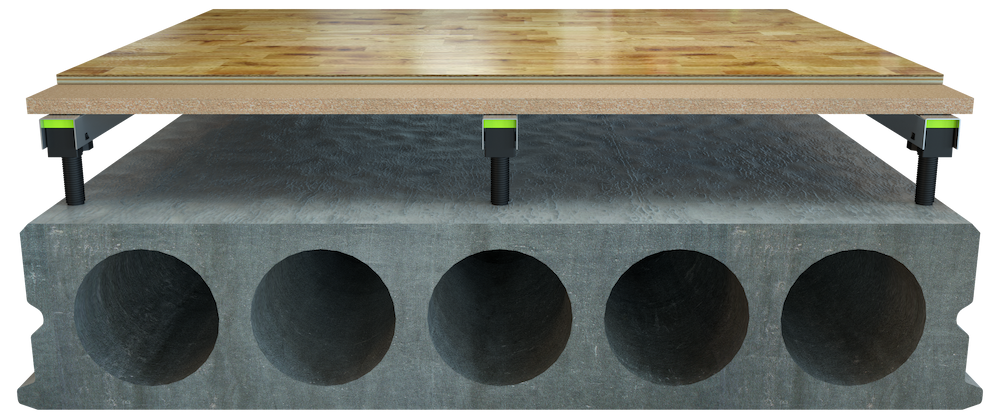
Design:
Granab subfloor system installed on HD/f 200mm and 22mm chipboard + 15mm parquet.
Result:
Impact sound: Lnw+c 48 dB, Airborne sound: Rw+c 61 dB.
Our systems




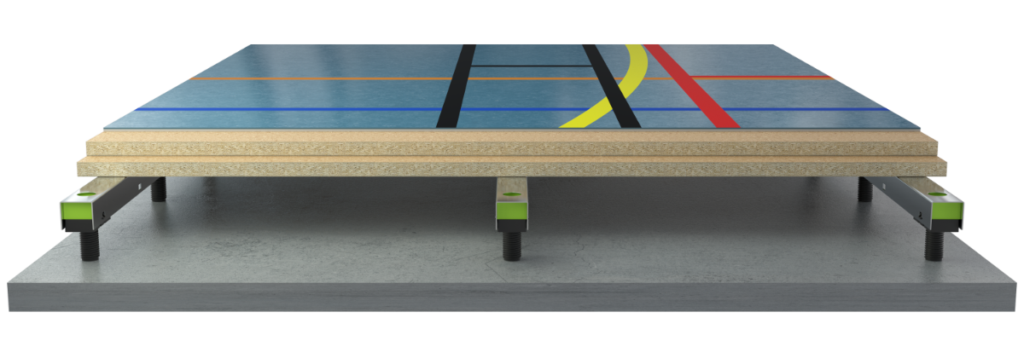
Sports floors
Eight unique Sports floors able to accommodate natural frequencies that are as low as 10Hz.
Read more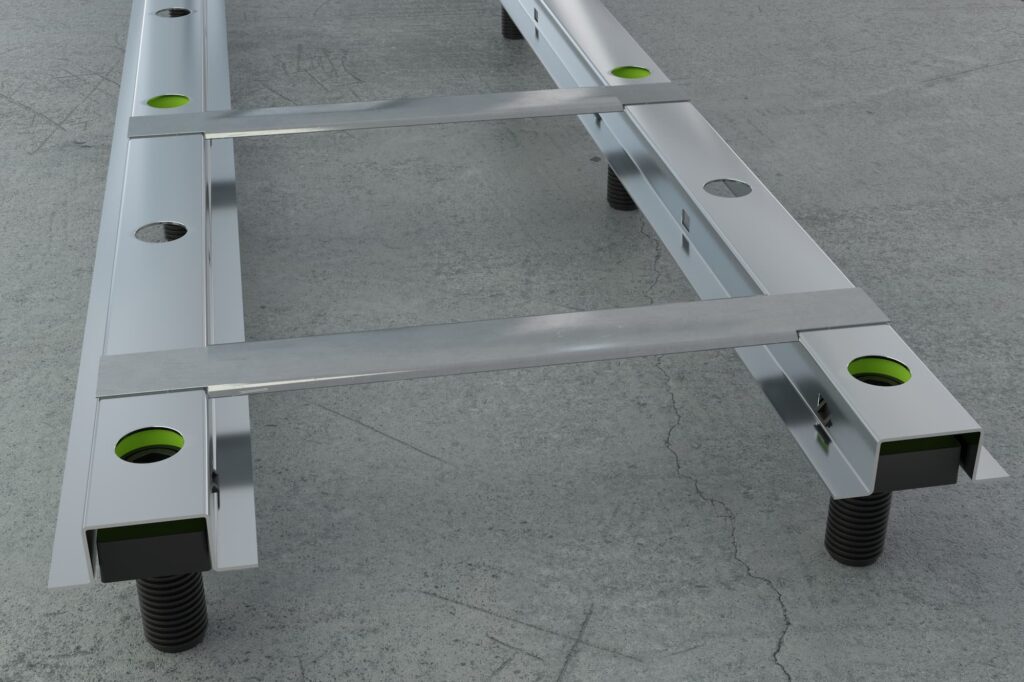
Environmental certification
Granab works actively to reduce environmental impact and has certifications that confirm our commitment to sustainability. All our subfloor systems have Environmentally Product Declarations (EPD).

